Assume that you’ve been assigned a task of calculating bond valuation; so if you are new to Ms Excel or do not have much experience with it, then I am pretty sure about it that doing this task manually might be your first approach, which is fine, but what will you do if you were assigned to compute bond valuation again and again with various values? If you still prefer to do it manually, then let me add that it will waste a lot of your time, and there is a probability that you will not be able to finish your task on time.
But don’t worry since you’ve just landed on the right article where you’ll learn an efficient approach to calculate bond valuation in a matter of seconds.
So, without further ado, let’s dive into it.
Table of Contents
General Formula:
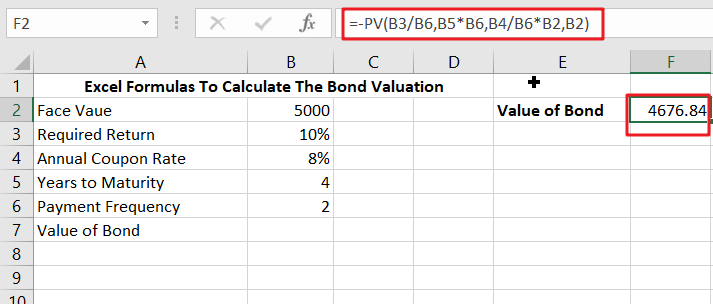
In Excel, use the formulae to compute the value of a bond on the issuance date.
=-PV(B3/B6,B5*B6,B4/B6*B2,B2)
Explanations of Syntax:
In order to use this formula to complete your task, you must be knowledgeable of the syntax used in that formula.
PV: The PV function in Excel is a financial tool that calculates the present value of an investment.Division (/): This symbol divides values or integers.The plus operator (+): This operator is used to add the values.Minus Operator (-): Use this symbol to subtract any two numbers.Multiplication (*): In this symbol, any two values or numbers will be multiplied.The comma symbol (,): This symbol is a separator that aids in the separation of a list of values.Parenthesis (): This symbol’s primary function is to group the elements.
Summary
The PV function may determine the value of a bond on the issuance date. In this post, we will look at two examples to better grasp the formula in F2. In the first case, the formula in F2 is as follows:
=-PV(B3/B6,B5*B6,B4/B6*B2,B2)

This example assumes that the issue date is today and that the next payment will be made in precisely 8 months. See the note below for information on calculating the value of a bond on any date.
Explanation
In the first example, we have a four-year bond with a $5,000 face value. Because the coupon rate is 8%, the bond will pay 8% of its face value in interest each year, or $400. However, because interest is paid in two equal installments semiannually, there will be eight $200 coupon payments. At maturity, the $5,000 will be repaid. Finally, the needed rate of return (discount rate) is set at 10%.
The present value of an asset’s cash flows is its worth. In this example, the PV function calculates the present value of the eight equal installments plus the $5000 payback when the bond matures. The PV function is set up as follows:
=-PV(B3/B6,B5*B6,B4/B6*B2,B2)
PV was given the following arguments:
- rate – B3/B6 =10%/2=5%
- nper – B5*B6=4*2=8
- pmt – B4/B6*B2=8%/2*5000=200
- fv – 5000
The PV function yields - 4676.84; thus, we apply a negative sign before the PV function to achieve the final result of $ 4676.84.
If you’re still confused, don’t worry because this second example will clear everything out for you.
In Example 2nd, we will see how to calculate bond valuation in Excel using the procedures below.
- This section will enter the input values in Columns A and B.
- Next, we will compute the value of a bond on the issuance date.
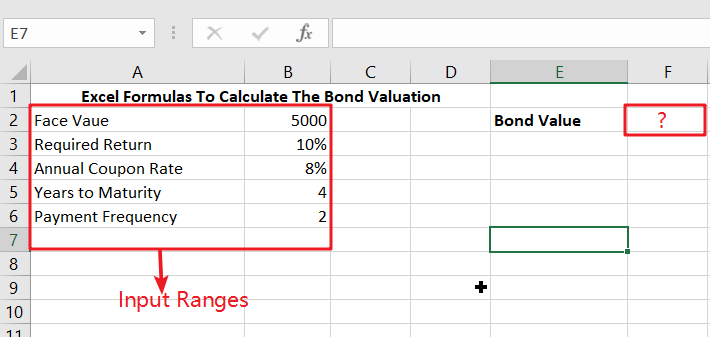
Ranges of Input
- In any cell, type the formula mentioned above.
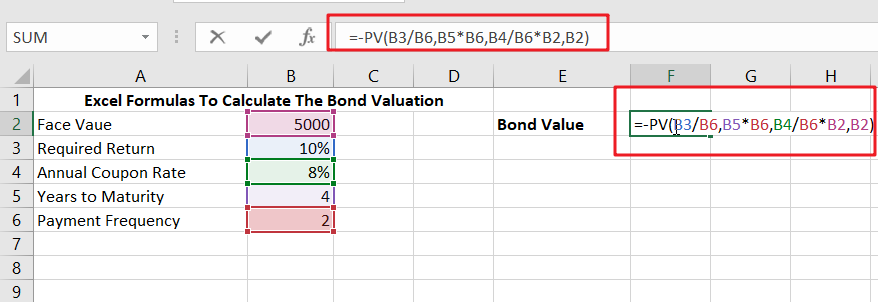
Enter the formula here.
- Finally, you will obtain the result displayed below when you press the ENTER key.

Between the payout dates of coupons
In the above example, using the PV function to calculate the value of a bond on a coupon payment date is pretty simple. Because interest does not compound between payments, determining the value of a bond between coupon payment dates is more complicated. The PRICE function may compute a bond’s “clean price” on any date.
Conclusion:
In this lesson, we explained the formulae for calculating the valuation of a bond on the issuance date in Excel using two practical examples.
Related Functions
- Excel PV function
The Excel PV function returns the present value of a loan or investment based on constant payments and a constant interest rate.The syntax of the PV function is as below:= PV(rate,nper,pmt,[fv],[type])
…