No repeat statistic based on a single condition is used wildly in daily work, for example, count type of products, the duplicate types are not encountered. This article describes the way of no repeats statistics for data in a single row or a single column using an array formula.
The example below shows the operation on a one-dimensional array with no repeat statistics.
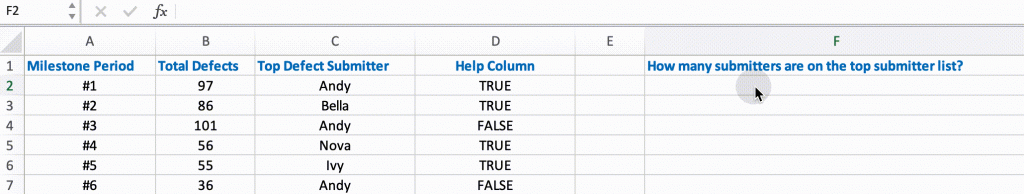
Buy some gifts to reward the top defect submitters for their contributions to the company. The core is to count how many submitters appear on this list with repeated submitters ignored.
Table of Contents
MATCH Function
Build a formula with EXCEL COUNT and MATCH functions:
=COUNT(1/(MATCH(C2:C7,C:C,0)=ROW(C2:C7)))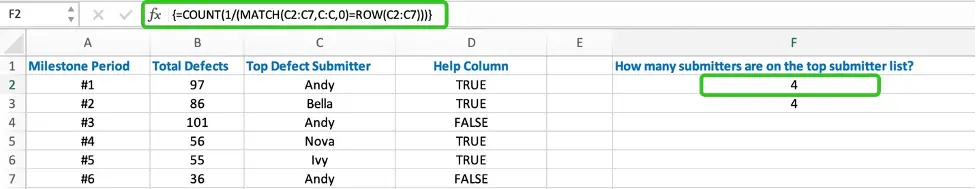
It is an array formula, so press Shift+Control+Enter to run it.
In this formula:
- The “Help Column” shows the logical values returned by the MATCH function.
- The MATCH function determines whether the submitter appears in the list for the first time. It returns logical
TRUEif it detects that the submitter does not appear in the range from the first cell to the cell above it, or logicalFALSEif the submitter already appears in the searched field.
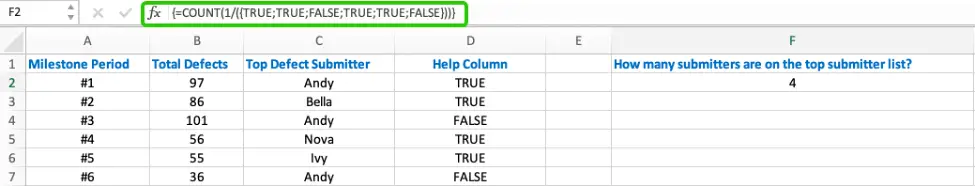
Use “1” divided by the logical value array to get a new array {1;1;#DIV/0!;1;1;#DIV/0!}.
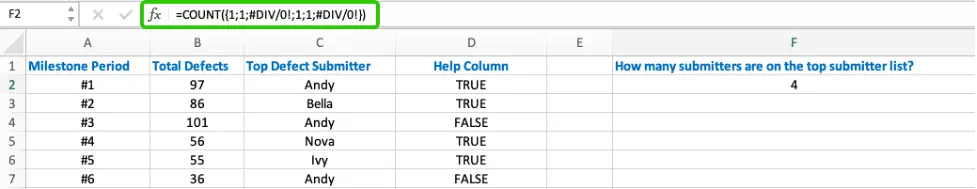
The COUNT function counts the numbers with errors ignored.
COUNTIF Function
We can also use EXCEL SUM and COUNTIF functions to count without repeats.
Build a formula with EXCEL SUM and COUNTIF functions:
=SUM(1/COUNTIF(C2:C7,C2:C7))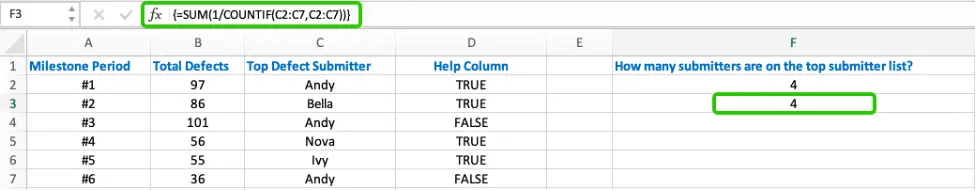
It is still an array formula, press Shift+Control+Enter to run it.
In this formula:
- COUNTIF(A:A,A:A) is a classic usage in statistics to count the number of occurrences of each value in column A.
- COUNTIF (C2:C7,C2:C7) returns an array that stores the number of occurrences of each submitter in the list. The array is {3;1;3;1;1;3}.
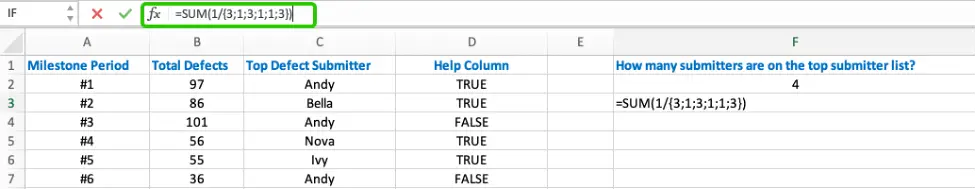
- Use “
1” divided by the array returned by COUNTIF function to get a new array{1/3;1;1/3;1;1;1/3}.
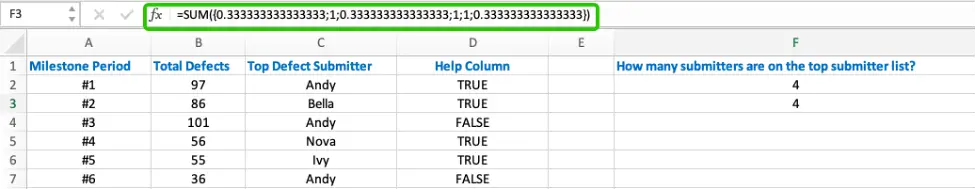
- The SUM function adds up the numbers in the array. For duplicate values, for example, Andy in the example,
1/3+1/3+1/3=1, so there are no duplicates in the count, which completes the statistics without duplicates.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.